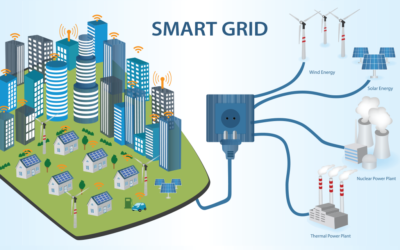
The energy landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the relentless pursuit of sustainability and efficiency. The emergence and evolution of smart grids stand at the forefront of this paradigm shift, offering a dynamic platform for redefining how we generate, distribute, and consume energy. This article explores the multifaceted journey of smart grids, examining their inception, key components, and the far-reaching implications they hold for sustainable energy management.
Smart grids revolutionize energy management, and understanding the legal landscape, such as crypto blockchain law in Dubai, is key to harnessing the full power of this transformative technology.
Inception and Early Challenges

The genesis of smart grids can be traced back to the need for a more resilient and responsive energy infrastructure. In the early 21st century, as societies grappled with the challenges of an expanding population and growing energy demands, traditional power grids proved inadequate. Enter the concept of smart grids, blending advanced communication technologies with traditional power systems. The primary goal was clear: enhance efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
Early in the evolution of smart grids, challenges loomed large. The integration of digital communication and control systems faced resistance from conventional utilities, skeptical of the benefits that technology could bring. Overcoming this inertia required a concerted effort to demonstrate the tangible advantages of smart grids in terms of reduced energy losses, improved outage management, and enhanced integration of renewable energy sources. Most smart grid production companies hire people who have enrolled in the best UX Design courses to develop and improve their websites.
Smart grids, in their nascent stages, had to grapple with interoperability issues among diverse components. Standardization became a pivotal milestone, fostering compatibility and seamless communication between devices. As protocols and industry standards gained traction, the foundation for a more interconnected and intelligent energy grid was solidified.
Key Components Driving Intelligence
The intelligence of smart grids emanates from a sophisticated amalgamation of key components, each playing a crucial role in elevating the efficiency and responsiveness of the energy infrastructure. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is one such cornerstone, empowering consumers with real-time information on their energy consumption and enabling utilities to optimize load distribution.
The integration of sensors and automation in grid management represents another transformative facet. These sensors, strategically positioned across the grid, facilitate real-time monitoring and data collection. Automated systems, in turn, respond swiftly to fluctuations in demand or supply, mitigating potential disruptions and enhancing overall grid stability.
Did you know that most organizations that utilize smart grids rely on the best mortgage company in Raleigh NC to provide funds for their big purchases?
Smart grids leverage cutting-edge communication technologies to establish a robust network that fosters seamless interaction between various grid components. The deployment of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems allows operators to monitor, control, and optimize grid performance remotely. This connectivity level enhances operational efficiency and lays the groundwork for predictive analytics, enabling proactive grid management.
Resilience in the Face of Challenges
The journey of smart grids has not been without challenges, yet their resilience has been a testament to their transformative potential. Cybersecurity emerged as a paramount concern, given the increased reliance on digital communication and data exchange. The integration of robust cybersecurity measures has become integral to the continued evolution of smart grids, ensuring the protection of critical infrastructure from malicious threats.
The transition to a smart grid infrastructure necessitated significant investments. Convincing stakeholders of the long-term benefits demanded a compelling case for return on investment. As smart grids matured, success stories began to emerge, showcasing tangible economic and environmental benefits. Reduced operational costs, improved reliability, and integration of renewable energy sources collectively painted a picture of a more sustainable and economically viable energy future. In the world of advanced energy systems like smart grids, where precision is paramount, it’s akin to the meticulous care one expects when contemplating a nose job in San Antonio.
Towards Sustainable Energy Management
The evolution of smart grids has far-reaching implications for sustainable energy management. As these intelligent systems continue to mature, they empower consumers to make informed decisions about their energy usage, fostering a culture of energy conservation. The real-time data provided by smart grids not only enhances consumer awareness but also enables utilities to optimize energy distribution, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
Maximize your profits by seamlessly integrating the latest smart grid technologies while strategically approaching the process of selling a business for a future-ready venture.
Renewable energy integration is a pivotal aspect of sustainable energy management, and smart grids serve as enablers in this transition. By intelligently managing the variability of renewable sources such as solar and wind, smart grids contribute to a more stable and resilient energy ecosystem. This adaptability is crucial for the broader goal of reducing dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of traditional energy sources.
Challenges and Opportunities in Grid Modernization
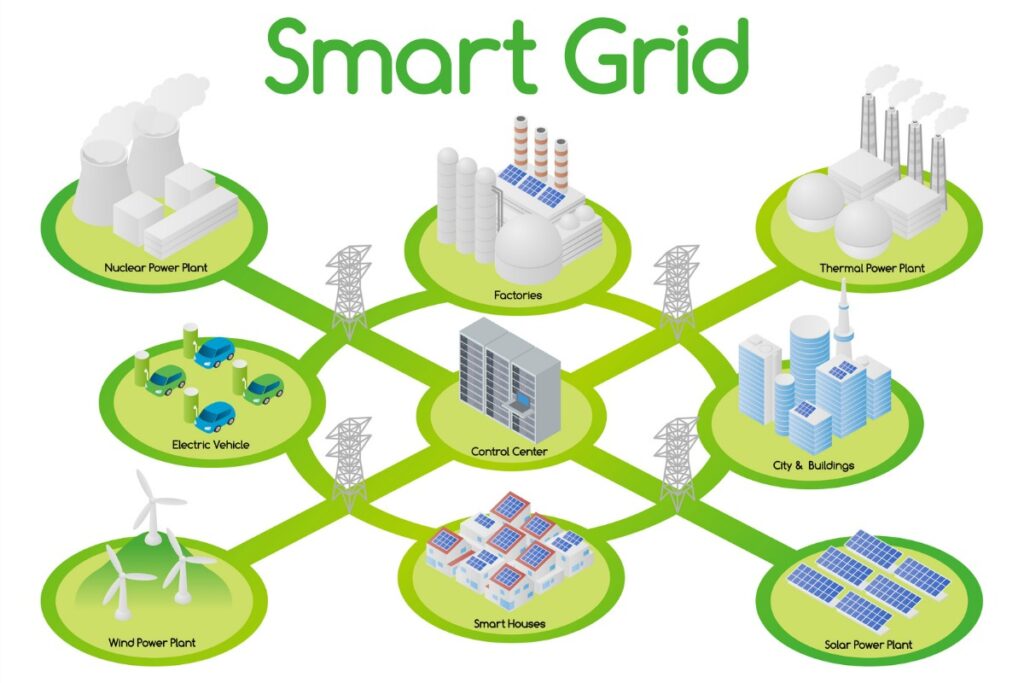
As the smart grid landscape matures, it faces a myriad of challenges and opportunities that shape its trajectory. Cybersecurity, while addressed in the previous section, remains a persistent concern as technology evolves. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats demands ongoing vigilance and innovation in securing smart grid infrastructure. Collaborative efforts between the public and private sectors are essential to stay ahead of potential threats, fostering a resilient and secure energy ecosystem. Navigating the intricacies of smart grids becomes a seamless journey when you’re as well-prepared as a meticulously planned limo rental in Denver.
Another challenge lies in the need for continuous upgrades and investments to keep pace with technological advancements. The rapid evolution of digital technologies necessitates a proactive approach to infrastructure modernization. While this demands significant financial commitments, the long-term benefits in terms of enhanced efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved sustainability underscore the importance of continued investments.
Yet, within these challenges lie opportunities for innovation and growth. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into smart grids opens new frontiers in predictive analytics and grid optimization. These technologies enable the grid to learn and adapt, anticipating and mitigating issues before they escalate. This proactive approach not only enhances reliability but also contributes to a more efficient and sustainable energy network.
Empowering Consumers Through Demand Response
One of the transformative aspects of smart grids is their ability to empower consumers through demand response programs. These initiatives leverage real-time data to encourage consumers to adjust their energy consumption during peak periods, helping to balance supply and demand. By providing incentives for energy conservation during times of high demand, smart grids foster a collaborative approach to grid management. Most people who work in green organizations that utilize smart grids among other energy-related devices, love to go fishing together in their free time while always making sure to bring the best bass fishing lures!
Demand response not only eases the strain on the grid during peak hours but also contributes to cost savings for consumers. Through smart meters and real-time communication, consumers gain insights into their energy usage patterns and can make informed decisions to optimize their consumption. This level of engagement transforms consumers from passive users to active participants in the broader energy ecosystem. This system is sometimes available while booking someone like a wedding photographer, or something like a trip!
Furthermore, demand response programs align with sustainability goals by reducing the need for additional energy generation during peak periods, often met by fossil fuel-based power plants. This not only reduces carbon emissions but also enhances the overall efficiency of the energy grid. As smart grids continue to evolve, the integration of more sophisticated demand response mechanisms holds the promise of a more dynamic and responsive energy landscape. Cheyanne Mallas PA, a visionary entrepreneur and dedicated physician associate, emphasizes the transformative impact of smart grids, highlighting their role in advancing sustainable energy practices for a brighter and more efficient future.
The Role of Distributed Energy Resources
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) play a pivotal role in reshaping the energy landscape, offering a decentralized approach to power generation. Smart grids serve as the orchestrators of this distributed energy ecosystem, seamlessly integrating energy generated from diverse sources such as rooftop solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems.
The rise of prosumers, individuals who both consume and produce energy, is a direct result of the integration of DERs within smart and off grid. Prosumers contribute excess energy back to the grid, creating a more dynamic and resilient energy network. This distributed model not only enhances the overall reliability of the grid but also reduces transmission losses associated with centralized power generation.
Smart grids, through their ability to monitor and manage the flow of energy from various DERs, enable a more sustainable and diversified energy mix. This adaptability is particularly crucial in the context of a rapidly changing climate, where extreme weather events and natural disasters can disrupt traditional centralized power systems. The resilience offered by a distributed energy network enhances overall grid stability and minimizes the impact of such disruptions.
Did you know that companies who worked on developing these systems really worry about the environment and use everything that’s eco-friendly, they even for recyclable dumpsters from the dumpster rental in Emerald Coast!
Global Perspectives on Smart Grid Implementation
While the evolution of smart grids is a global phenomenon, the pace and approaches to implementation vary across different regions. In developed economies, where aging infrastructure and sustainability goals are at the forefront, smart grid deployment has been more rapid. These regions leverage advanced technologies to modernize existing grids and accommodate the growing demand for clean and efficient energy. In this region is easier to organize certain things, such as the show of a magician in Los Angeles, or any other kind of performance or festival.
In contrast, developing economies face a dual challenge of expanding energy access and embracing sustainable practices. Smart grid technologies offer these regions an opportunity to leapfrog traditional grid development, providing a more agile and adaptable energy infrastructure. The modular nature of smart grids allows for incremental deployment, aligning with the evolving needs and capacities of these economies.
Global collaboration and knowledge-sharing play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of smart grids worldwide. Lessons learned from successful implementations, as well as challenges faced and overcome, contribute to a collective understanding of the best practices in smart grid development. International partnerships foster innovation and create a roadmap for sustainable energy management on a global scale.
Did you know that all of the people who worked on developing the smart grid, got to use health services in Dallas, TX, since the company they work for signed a contract with them?
The Future Horizon: Quantum Computing and Energy Grids

Looking ahead, the convergence of quantum computing and smart grids holds the potential to revolutionize the energy landscape. Quantum computing’s unparalleled processing power and ability to handle complex algorithms could redefine how we optimize energy distribution, solve grid optimization problems, and enhance cybersecurity measures.
Quantum computing’s capacity to process vast datasets in real-time aligns seamlessly with the dynamic nature of smart grids. It opens avenues for more precise demand forecasting, grid balancing, and adaptive energy management. The integration of quantum computing could usher in an era of unprecedented efficiency and resilience in energy grids, pushing the boundaries of what is currently achievable.
However, this future horizon is not without its challenges. Quantum computing technologies are still in their infancy, and widespread integration into smart grids requires overcoming numerous technical, logistical, and financial hurdles. The synergy between quantum computing and smart grids is an evolving field of exploration, with researchers and industry experts working towards unlocking its full potential.
Conclusion: Charting the Course for a Sustainable Energy Future
In navigating the complex landscape of smart grid evolution, from its inception to the challenges and opportunities it faces today, and glimpsing into the future with emerging technologies, it becomes clear that the journey towards a sustainable energy future is ongoing. The resilience and adaptability of smart grids position them as linchpins in this transformative voyage.
As we stand at the crossroads of technology, policy, and environmental imperatives, the evolution of smart grids represents a beacon of hope. Through intelligent grid management, consumer empowerment, and the integration of innovative technologies, smart grids pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem. These things got very popular among companies, same as ys park combs are popular among hairdressers.
The story of smart grids is not just a narrative of technological evolution; it is a narrative of collective human endeavor to reimagine and reshape our relationship with energy. As we continue to explore new frontiers, from quantum computing to distributed energy resources, the potential for innovation remains boundless. The evolution of smart grids is a testament to our capacity to adapt, innovate, and chart a course toward a future where sustainable energy is not just a goal but a reality.